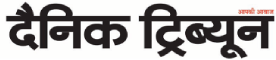Donald Trump with Saudi Arabia''s Crown Prince Muhammad bin Nayef (3rd R), in Riyadh. Trump is fuelling divisions. Reuters
Muhammad Amir Rana
FREED from Al-Qaida in 2001, the Tora Bora caves and the tunnels in Afghanistan have now fallen to violent extremists linked to the militant Islamic State (IS) group. This strategic "victory" for the terrorist group came after the US dropped the so-called mother of all bombs in April on its hideouts, a network of tunnels in Afghanistan. The IS march in Afghanistan has once again proved that finding new physical spaces is not a major issue for the terrorists; many conflict-ridden, ungoverned, and poorly administered territories are available — from the sub-Saharan region to the tribal areas in the Arabian Peninsula, from the bordering region between Afghanistan and Pakistan to the Philippines.
As the terrorists continue to mount threats to physical security, the response is also expected to remain focused on employing greater force. This is also making it more challenging for Muslim power elites to take on the terrorists in their ideological and intellectual spaces. The Trump administration's renewed focus on hard approaches to countering terrorism could provide these elites with more excuses to continue living in their mental comfort zones. Ironically, the claimants of Muslims' religious leadership, Saudi Arabia and Iran, are accusing each other of supporting terrorism. However, the Saudi and Iranian counter-terrorism mantras and alliances are nothing more than efforts to secure their own petty political and strategic interests — at the cost of the lives of those these two countries claim to lead. The IS is a manifestation of the intellectual bankruptcy of the Muslim ruling elites. Their actions are not only bringing trouble to themselves but are also fuelling sectarian tensions in Muslim societies and polarising Muslim-majority nations by forcing them to choose sides. This is an appalling situation, mainly for many Muslim states including Pakistan, which are struggling to adjust to the strategic and economic meltdown in the Middle East.
The real challenge thus is not the expansion of the IS in physical spaces, but the mindset of the ruling elites and their partners, ie the clergy, which is scared of new ideas. They don't realise that their traditionalism and orthodoxy are eroding their own foundations. The need to evolve intellectual responses for countering extremism notwithstanding, a review of collective wisdom and its expressions is also important, mainly to measure a nation's level of resilience and maturity. Parliament is the true representative of the collective wisdom of Pakistanis. It has recently suggested a neutral role for Pakistan in the Middle-East crisis. Similar parliamentary advice came on the Yemen crisis. The policymakers and media of both Saudi Arabia and UAE criticised this stance. A statement circulating on social media, attributed to a top Saudi official, that criticised Pakistani neutrality and parliament, should not be surprising because many believe that our Arab brothers are not interested in Pakistan's democratic credentials, but in the country's military power. Let's not forget that when parliament took a neutral position on Yemen, the UAE tried to punish Pakistan through developing a strategic partnership with India, although it knew that India could not support their misadventure in Yemen. Many opinion makers in Arab countries also accused Pakistan for “using” parliament as an excuse to not send its troops for military adventures. Though in that case parliament proved a blessing for the establishment, the maturity it has shown over the issue is commendable. However, the actual challenge for parliament is to build intellectual and policy capital. One can debate the capacity of parliamentarians and the government's somewhat indifferent attitude towards parliament, but this is still the institution which is keeping the country cohesive. This is the institution which should address the issue of extremism and the IS in our minds.
Parliament can take the lead in nurturing the process of inclusive nation-building, by initiating debates on the extent to which diversity has been dissipated by policies of the past and incorporating the voices of different groups in the country. Parliament can draw an outline of a fresh national narrative. It can engage with all departments or institutions of the government, informing them of the consequences of their actions on social diversity. An active and effective parliament can fill the spaces which exist in our thoughts and that are exploited by multiple ideological players including the IS. It is recognised that terrorist groups are more afraid of non-violent, soft measures than hard measures. They exploit hard measures by pushing the narrative of the “victimhood of Islamic forces” to justify both their existence and their violent acts. Their reaction is stronger if someone challenges their narrative; be it religious scholars, the media or opinion makers. There are plenty of examples available that they hit hard those who challenge their arguments. The content analysis of any militant publication would be helpful to understand the ideological paraphernalia of a terrorist group. For example, an old issue of Ahya-i-Khilafat (Revival of the Caliphate), a mouthpiece of the Tehreek-i-Taliban Pakistan, consisted of 15 articles, including an interview with its leader and profile of a leading commander. Four articles were dedicated to their operations and so-called successes, two were against secularism, two detailed articles were meant to elaborate and glorify the caliphate system; but four articles were allocated to build their case against democracy and parliament. One article titled “I am a constitutional man” was a satire on religious political leaders, ie what did it mean (for the militants) in religious terms when these leaders said they believed in a constitutional democracy. Parliament is a target of non-state actors and our Arab friends are also not happy with the institution on different grounds. One is not sure whether or not our parliamentarians know their importance and the role they have to play in developing a moderate and inclusive Pakistan. If parliament fails, it will fail the nation.
By arrangement with the Dawn