For representation only. Photo source: Thinkstock
London
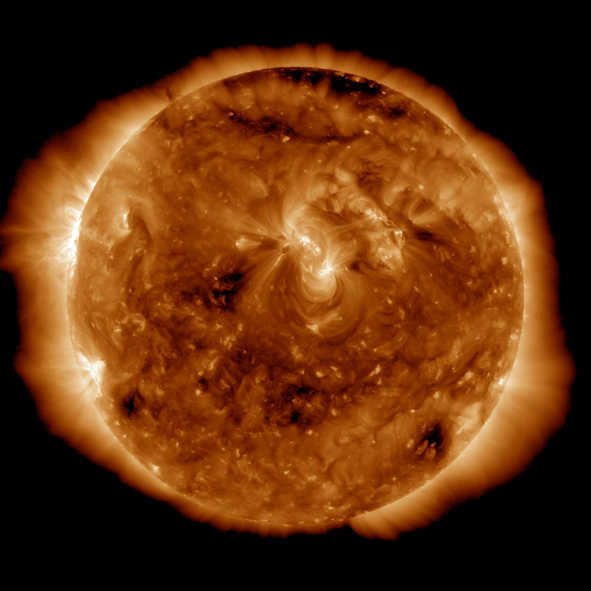
Scientists have found a star that is almost identical to the Sun, except for the chemical composition, making it a 'Rosetta Stone' for the study of the solar body's variability and effect on the Earth's climate.
The spots on the surface of the Sun come and go with an 11-year periodicity known as the solar cycle.
The solar cycle is driven by the solar dynamo, which is an interplay between magnetic fields, convection and rotation.
However, our understanding of the physics underlying the solar dynamo is far from complete.
Now, an international team led by researchers from Aarhus University in Denmark has found a star that can help shed light on the physics underlying the solar dynamo.
The star is located 120 light years away in the constellation of Cygnus, and on the surface, the star looks just like the Sun: it has the same mass, radius and age—but its chemical composition is very different.
It consists of around twice as many heavy elements as in the Sun. Heavy elements are the ones heavier than hydrogen and helium.
The new study can help us understand how the irradiance of the Sun has changed over time, which is likely to have an effect on our climate, researchers said.
The team has succeeded in combining observations from the Kepler spacecraft with ground-based observations dating as far back as 1978, thereby reconstructing a 7.4-year cycle in this star.
"The unique combination of a star almost identical to the Sun, except for the chemical composition, with a cycle that has been observed from both the Kepler spacecraft and from ground makes this star a Rosetta Stone for the study of stellar dynamos," said Christoffer Karoff from Aarhus University.
By combining photometric, spectroscopic and asteroseismic data, the team collected the most detailed set of observations for a solar-like cycle in any star other than the Sun.
The observations revealed that the amplitude of the cycle seen in the star's magnetic field is more than twice as strong as what is seen on the Sun, and the cycle is even stronger in visible light.
This allowed the team to conclude that more heavy elements make a stronger cycle. PTI