Dr Kavita Ramanathan
Diabetes has become a major public health challenge in India. Estimates put the prevalence of the disease to be over 6 per cent of India’s population older than 18 years. India being home to more than a sixth of world population, the estimates indicate a diabetes affected population size of over seven crore people.
Often called the “silent killer” most people don’t realise about the onset of diabetes or how associated factors such as obesity, hypertension, can raise the risk of the disease. Most of its symptoms are easy to miss, and often diabetes remains undetected for a long time. The common symptoms include frequent need for urination, increased thirst, unexpected weight loss, cravings for carbohydrates-rich food or sugar, exhaustion, and prolonged obesity.
This is especially true for developing countries like India where the huge human population is adapting to the changing lifestyle patterns, hectic schedules, increased levels of comfort, decreasing physical mobility, exposure to a massive range of high-calorie dietary options at cheap prices, and increasing intake of alcohol and smoking.
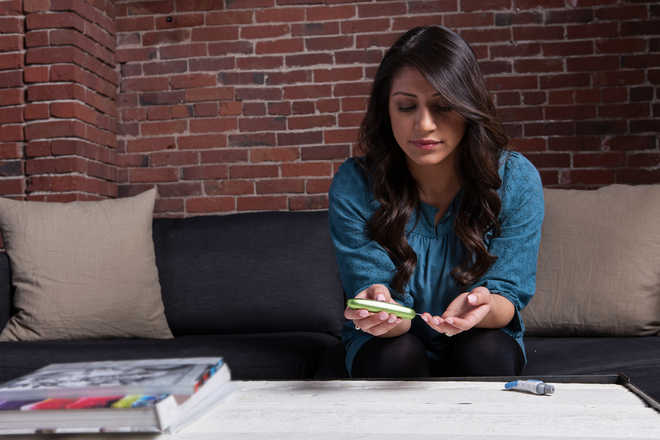
Given the context, regular and timely tests and check-up the only way to know whether one has diabetes or not.
Essential tests
Basic blood sugar tests are an important diagnostic measure to identify whether a patient is diabetic. Broadly categorised as four types, these tests have crucial differences. These include fasting blood sugar test, two-hour postprandial test (or two hours after breaking fast), random blood sugar tests and haemoglobin A1C test.
Haemoglobin A1C test (HbA1C): A form of protein found in the red blood cells, haemoglobin is the oxygen carrier in the blood. One of the most important tests, HbA1C test tells us about the average sugar levels in the blood. Sugar which exists in blood in the form of glucose binds to haemoglobin, which HbA1C test measures. It helps in determining whether a person is at pre-diabetes stage or how effective the medicines of a diabetic patient are. The normal range of blood haemoglobin A1C test result is between 4 and 5.6 per cent; from 5.6 to 6.4 levels tell that a person is at a higher chance of getting diabetes; and level of more than 6.5 per cent indicates the person has diabetes. Haemoglobin A1C test result levels more than 8 per cent indicates that blood sugar is not under control. Fasting blood sugar test: It is important to conduct this test when the patient has not eaten anything for the past eight to 12 hours. It measures glucose levels in the blood to determine diabetes or pre-diabetes. This should be done at least two times a year for normal person. Diabetes patients will have more frequent testing needs as prescribed by the consulting doctor.
Two-hour postprandial test: This test (prandial means meal) helps in assessing whether the blood glucose levels return to normal levels after having a meal. This is crucial as it gives insight on how the body is managing the glucose levels after meals. Normal range for this test is around 70-145 mg/dL (less than 7.9 mmol/L).
Random blood sugar test: In healthy individuals random blood sugar tests will give relatively stable results. In diabetics or pre-diabetics, this test will indicate different sugar levels, especially if glucose is not well controlled. Therefore, it is an important tool to determine whether the disease management is actually working.
Other tests
Diabetes can lead to other diseases and complications, including loss of sight, cardiovascular and kidney diseases. There are many tests important for a diabetes patient which can help to manage the disease. These include getting your lipid or cholesterol levels checked to evaluate the risk of cardiovascular diseases. For kidneys, microalbumin test measures the ratio of albumin (a protein) levels to the creatinine levels, a waste product. This ratio indicates if kidneys are functioning properly. It should be conducted at least once a year. High blood sugar levels damage blood vessels in the eyes leading to gradual vision loss. Therefore, go for eye annual eye check-up. Also get the blood pressure checked regularly.
Prevention remains the key
Diabetes has no known cure and can only be managed. Certain consequences of the disease are almost unavoidable with progressing age. Everything comes down to two things, prevention and management, and both have the same solutions. Lifestyle changes, physical mobility, and following healthy dietary practices can’t be stressed enough. At the same time, to keep a tab on the health, it is essential to see these common diagnostic tests as preventive measures rather than curative measures, given that these help in alerting us to lead a healthy life.
— The writer is senior pathologist,
iGenetic Diagnostics